Request
- request.method: 获取请求方式
- request.GET: 获取 GET 请求的参数
- request.POST: 获取 POST 请求的参数
GET & POST
POST 请求通常用于实现对后台数据库数据的更改, 一旦更改完毕, 便通常以一个 redirect 的形式返回到目标页面
Whenever you create a form that alters data server-side, use method=“post”.
As the Python comment above points out, you should always return an HttpResponseRedirect after successfully dealing with POST data.
Post Request
<form action="{% url 'polls:vote' question.id %}" method="post">
{% comment %} In short, all POST forms that are targeted at internal URLs should use the {% csrf_token %} template tag. {% endcomment %}
{% csrf_token %}
<fieldset>
<legend><h1>{{ question.question_text }}</h1></legend>
{% if error_message %}<p><strong>{{ error_message }}</strong></p>{% endif %}
{% for choice in question.choice_set.all %}
<input type="radio" name="choice" id="choice{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id }}">
<label for="choice{{ forloop.counter }}">{{ choice.choice_text }}</label><br>
{% endfor %}
</fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="Vote">
</form>通过 Form 实现 Post 请求:
- action 支持非硬编码 url; action 默认将请求传给当前 url;
- input 标签中的 name 属性为 POST 的键名, value 属性为 POST 的键值
- label 标签的指向, 更人性化的选取
- csrf 防止跨站请求伪造
csrf 防止跨站请求伪造
POST 请求时会自动传递 csrfmiddlewaretoken 这个参数, 生存期仅一次
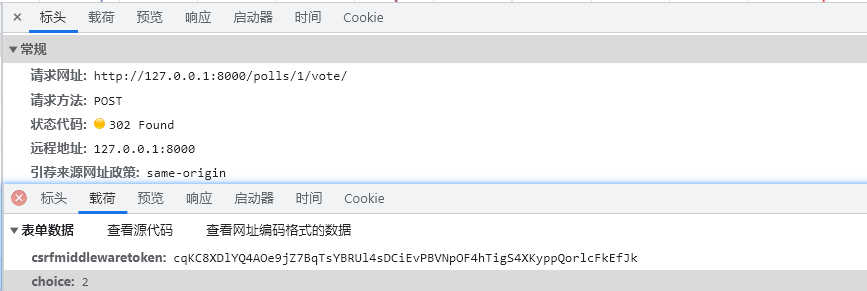
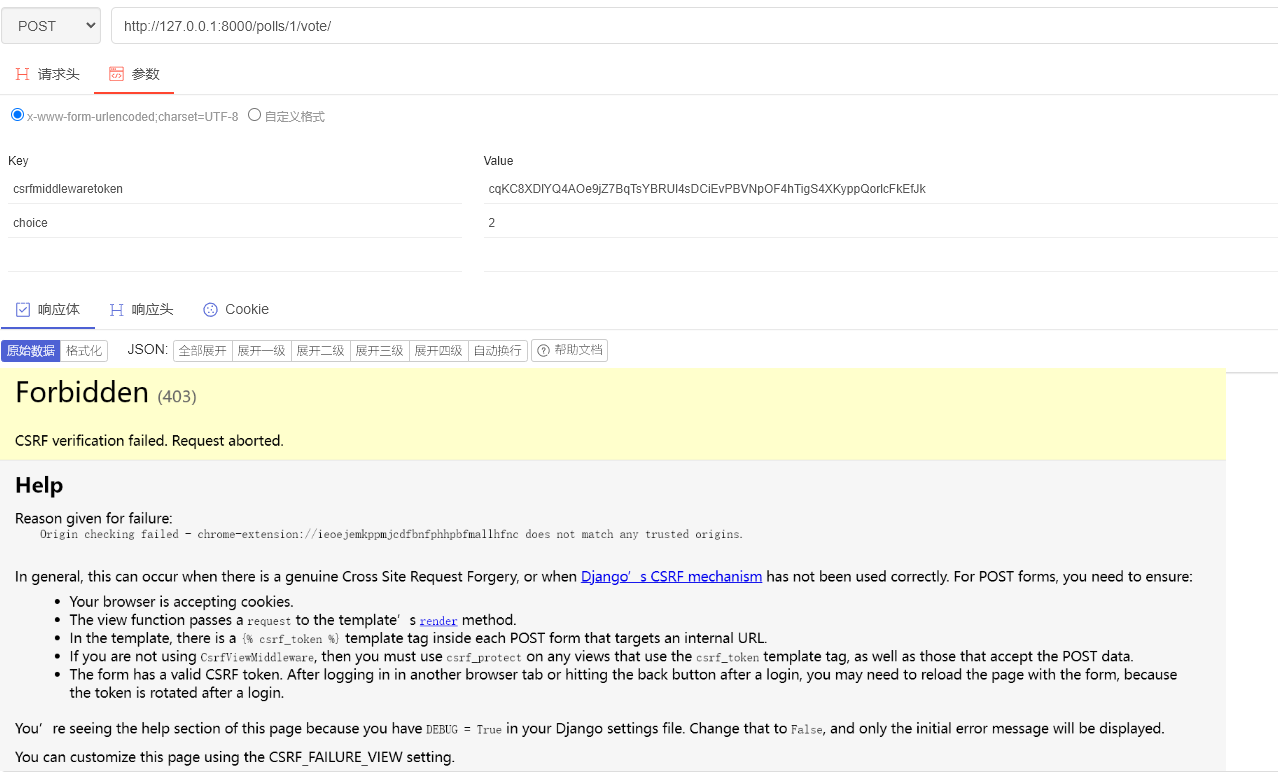
如果使用其它工具直接重现请求: 如 Postman, 直接失败
Post Redirect
def vote(request, pk):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=pk)
try:
selected_choice = question.choice_set.get(pk=request.POST['choice'])
except (KeyError, Choice.DoesNotExist):
return render(request, 'polls/detail.html', {
'question': question,
'error_message': "You didn't select a choice.",
})
else:
selected_choice.votes += 1
selected_choice.save()
# reverse function helps avoid having to hardcode a URL in the view function.
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls:results', args=(question.id,)))- 注意后台处理中数据库数据的 selected_choice 并没有添加互斥所, 多个用户同时请求更新这个数据时可能会出现错误, 解决方案后续更新…
- reverse 函数解决了目标 url 的硬编码问题; 当然可以直接使用
django.shortcuts.redirect