控件基础知识
宽度高度的取值
match_parent: 由父布局来决定当前控件的大小wrap_content: 由控件内容决定当前控件的大小- 固定值: 单位一般用 dp(一种屏幕密度无关的尺寸单位, 可以保证在不同分辨率的手机上显示效果尽可能地一致)
可见性的取值
visible: 可见invisible: 不可见, 但是仍然占据着原来的位置和大小gone: 不可见, 且不再占用任何屏幕空间
基础控件
Button
- 按钮中字母大写:
:textAllCaps: "true"
事件
setOnClickListener: 单击事件
button1.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(this, "You click Button 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}事件的统一处理接口
将 Button 的点击事件统一交给 Activity 处理
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), View.OnClickListener {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val button_1 = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button_1)
val button_2 = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button_2)
button_1.setOnClickListener(this)
button_2.setOnClickListener(this)
}
override fun onClick(view: View?) {
Log.d("TEMP", (view == null).toString())
when (view?.id) {
R.id.button_1 -> {
Toast.makeText(this, "Button 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
R.id.button_2 -> {
Toast.makeText(this, "Button 2", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
else -> {
Toast.makeText(this, "Button None", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
}TextView
- 文字对齐方式:
:gravity, 取值有(top, bottom, start, end, center); 使用|同时指定多个值 - 文字颜色:
:textColor="#00ff00" - 文字大小:
:textSize="24sp"使用 sp 作为单位,这样当用户在系统中修改了文字显示尺寸时,应用程序中的文字大小也会跟着变化
Toast
在窗口中进行提示 Toast.makeText(Context, Content, Time):
- Context:Toast 要求的上下文,由于 Activity 本身就是一个 Context 对象,因此通常为 this
- Content: 显示的文本内容
- Time: 显示的时长,有两个内置常量可以选择:
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT和Toast.LENGTH_LONG
Toast.makeText(this, "You click Button 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()Menu
- 新建 menu 资源:
res/menu+res/menu/Menu_Resource_File_Name - 在
Menu_Resource_File_Name进行资源的添加: `
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id="@+id/add_item"
android:title="Add"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/remove_item"
android:title="Remove"/>
</menu>- 重写 Activity 中的
onCreateOptionsMenu()方法- 传入的 menu 指向的是当前 Activity 的菜单对象实例
menuInflater实际上调用了父类中的getMenuInflater()方法获取到MenuInflater对象- 然后调用
inflate()方法给当前 Activity 创建菜单: 第一个参数为菜单资源,第二个参数为菜单上下文 - 返回 true 表示菜单创建后显示出来
override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu?): Boolean {
menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.main, menu)
return true
}响应事件
- 菜单项被点击:
onOptionsItemSelected()
// 菜单响应事件
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
when (item.itemId) {
R.id.add_item -> Toast.makeText(this, "You clicked Add", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
R.id.remove_item -> Toast.makeText(this, "You clicked Remove", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item)
}图标和位置
在布局文件中通过 icon 属性指定菜单选项的图标, 通过 showAsAction 属性指定菜单选项的展示位置
- always: 表示永远显示在 Toolbar 中, 空间不够则不显示
- ifRoom: 表示优先显示在 Toolbar 中, 空间不够显示在菜单中
- never: 表示只显示在菜单中
<item
android:id="@+id/backup"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_backup"
android:title="Backup"
app:showAsAction="always" />PopupMenu
自定义弹出的 Menu 菜单

- 准备 Menu 的资源文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id="@+id/menu_info_by_day"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_meteor_64"
android:title="星迹" />
<item
android:id="@+id/menu_export_db"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_db_export_64"
android:title="导出数据" />
<item
android:id="@+id/menu_import_db"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_db_import_64"
android:title="导入数据" />
</menu>- 初始化: 初始化时指定其弹出的位置(通过一个 view 对象指定)如果空间足够,它会显示在锚定 View 下方,否则显示在其上方
val popupMenu by lazy {
val menu = PopupMenu(this, toolbarFragment.viewShowMenu) // 指定其弹出的位置
menu.menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.main_config, menu.menu)
menu
}- 配置点击事件: 返回 True 表示点击事件被消耗
popupMenu.setOnMenuItemClickListener {
when(it.itemId) {
R.id.menu_info_by_day -> {
TodoItemInfoByDayActivity.onActionStart(this)
true
}
else -> {
true
}
}
}- 配置点击显示 Menu: 使用 MenuPopupHelper 进一步封装, 是为了在每一个 Menu 项中显示 Icon
setForceShowIcon(true)
val menu = MenuPopupHelper(this,
(popupMenu.getMenu() as MenuBuilder), toolbarFragment.viewShowMenu)
menu.setForceShowIcon(true)
menu.show()EditText
- 提示内容:
:hint="Type something here" - 最大行数:
:maxLines="1"超过最大行数会滚动显示(组件不会拉伸) - 内容过滤模板:
:inputType常用的有text, textPassword, number
方法:
- 获取内容:
edit_username.text.toString() - 设置内容:
edit_username.setText(String) - 设置光标位置:
edit_username.setSelection(Int) - 请求 Focus:
requestFocus() - 全选:
selectAll()
ImageView
-
设定图片源:
:src="@drawable/image_demo_1" -
修改图片源:
.setImageResource(R.drawable.image_demo_2)
ProgressBar
进度条样式
- 默认旋转加载进度条
- 水平进度条:
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"- 设定进度最大值:
:max="100" - 设定初始进度值:
:progress="50" - 获取进度值:
int progress = progressBarHorizontal.getProgress(); - 设置进度值:
progressBarHorizontal.setProgress(progress);
- 设定进度最大值:
AlertDialog
在当前界面弹出一个对话框, 置于所有界面元素之上(屏蔽其他控件的交互能力)
二次确认
R.id.button_change_image -> {
val environment = this
AlertDialog.Builder(this).apply {
setTitle("Warning")
setMessage("Do you really want to change the image source?")
// 可否使用 Back 键关闭对话框
setCancelable(true)
setPositiveButton("YES") { dialog, which ->
Toast.makeText(environment, "Change Image", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
val image_demo_1 = findViewById<ImageView>(R.id.image_demo_1)
image_demo_1.setImageResource(R.drawable.image_demo_2)
}
setNegativeButton("Cancel") { dialog, which -> dialog.dismiss()}
show()
}
}列表选择
val todoCategoryItems = viewModel.todoCategoryList.map { it.name }.toTypedArray()
val alertBuilder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(this).apply {
setTitle("时间规划集")
.setItems(todoCategoryItems, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, which ->
insertTodoitmeCategory.setText(todoCategoryItems.get(which))
dialog.dismiss()
})
create()
show()
}
ProgressDialog【OLD】
功能:弹出的对话框中显示一个进度条,缓解用户等待的焦躁。
构建方法:与AlertDialog类似
ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("Progress Dialog");
progressDialog.setMessage("Loading...");
progressDialog.setCancelable(true);
progressDialog.show();布局
LinearLayout
- 布局方向:
:orientation属性排列方向有vertical, horizontal - 对齐方式:
:layout_gravity和文字在空间中的对齐方式类似- 水平排列时, 水平长度不固定, 因此
center会失效; 同理, …
- 水平排列时, 水平长度不固定, 因此
- 空间比例排布:
:layout_weight="1"在一行或一列中按照比例分配大小, 自适应拉伸; 需要将:layout_width置为 0
布局技巧: 先 Layout 后 组件
RelativeLayout
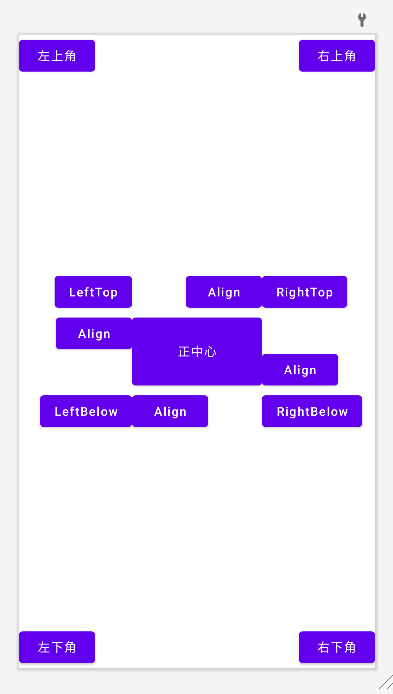
通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置
根据父组件布局:
:layout_alignParentLeft="true":layout_alignParentRight="true":layout_centerInParent="true":layout_alignParentTop="true":layout_alignParenBottom="true"
根据某一组件的位置布局:
:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button_center":layout_toLefttOf="@+id/button_center":layout_above="@+id/button_center":layout_below="@+id/button_center"
相对于组件对齐:
:layout_alignLeft: 两组件左边缘对齐:layout_alignRight: 两组件右边缘对齐:layout_alignTop: 两组件上边缘对齐:layout_alignBottom: 两组件下边缘对齐
FrameLayout
帧布局, 所有的控件都会默认摆放在布局的左上角

自定义控件
所有控件都是直接或间接继承自 View:
- View 是 Android 中最基本的一种 UI 组件,它可以在屏幕上绘制一块矩形区域,并能响应这块区域的各种事件

Application:
- 公共组件的复用
<include layout="@layout/title" />: 标题栏, 尾部栏- 需要将系统自带的标题栏等进行隐藏:
supportActionBar?.hide()
- 需要将系统自带的标题栏等进行隐藏:
- 但是如果复用的组件中有交互性事件, 如何复用这些事件的响应操作呢, 引入了自定义控件
class TitleLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : LinearLayout(context, attrs) {
init {
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.title, this)
val titleBack = findViewById<Button>(R.id.titleBack)
val titleText = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.titleText)
val titleEdit = findViewById<Button>(R.id.titleEdit)
titleBack.setOnClickListener {
val activity = context as Activity
activity.finish()
}
titleEdit.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(context, "Editing...", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}LayoutInflater对象用于实现动态加载, 通过LayoutInflater的from()方法可以构建出一个LayoutInflater对象,然后调用inflate()方法就可以动态加载一个布局文件- 第一个参数是要加载的布局文件的 id
- 第二个参数是给加载好的布局再添加一个父布局,这里我们想要指定为 TitleLayout,于是直接传入 this
在布局文件中添加这个自定义控件, 即可将相关的事件处理也一并复用引入:
<com.example.a05_uicustomviews.TitleLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>ListView
ListView 允许用户通过手指上下滑动的方式将屏幕外的数据滚动到屏幕内,同时屏幕上原有的数据会滚动出屏幕
Quick Start
- 准备好数据
private val data = listOf("Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Watermelon",
"Pear", "Grape", "Pineapple", "Strawberry", "Cherry", "Mango",
"Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Watermelon", "Pear", "Grape",
"Pineapple", "Strawberry", "Cherry", "Mango")- 封装到 adapter 中
val adapter = ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, data)- 泛型通过数据类型指定为
String - Context 参数为当前 Activity
- resource: 参数指的是数据项的布局 id, 这里我们使用内置的 simple_list_item_1
- 设置 adapter 到 listview 中
list_main.adapter = adapteradapter
适配器, 是数据项与视图(展示)的桥梁, 即 MVC 中的 C(Controller): An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view. The Adapter provides access to the data items. The Adapter is also responsible for making a View for each item in the data set.

常用有 ArrayAdapter, CursorAdapter, SimpleCursorAdapter 不同的类定义了不同的数据展示形式
自定义 adapter
主要是自定义数据项的显示界面
- 首先对我们的数据项中的数据进行封装
class Fruit(val name:String, val imageId: Int) {
}- 然后编写数据项的 Layout (作为 Adapter 的参数)
<!-- 左图右文字 -->
<LinearLayout ...>
<ImageView .../>
<TextView .../>
</LinearLayout>- 自定义 Adapter: 在 ArrayAdapter 的基础上自定义展示视图
class FruitAdapter(activity: Activity, val resourceId: Int, data: List<Fruit>): ArrayAdapter<Fruit>(activity, resourceId, data) {
inner class ViewHolder(val fruitImage: ImageView, val fruitName: TextView)
override fun getView(position: Int, convertView: View?, parent: ViewGroup): View {
val view: View
val viewHolder: ViewHolder
if (convertView == null) {
view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(resourceId, parent, false)
val image_fruit_item: ImageView = view.findViewById(R.id.image_fruit_item)
val text_fruit_name:TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_fruit_name)
viewHolder = ViewHolder((image_fruit_item, text_fruit_name))
view.tag = viewHolder
} else {
view = convertView
viewHolder = view.tag as ViewHolder
}
val fruit = getItem(position)
if (fruit != null) {
viewHolder.fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.imageId)
viewHolder.fruitName.text = fruit.name
}
return view
}
}- Apply Adapter to data
private val fruitList = ArrayList<Fruit>()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
supportActionBar?.hide()
val list_main = findViewById<ListView>(R.id.list_main)
initFruits()
val adapter = FruitAdapter(this, R.layout.fruit_item, fruitList)
list_main.adapter = adapter
}
private fun initFruits() {
repeat(2) {
fruitList.add(Fruit("Cherry", R.drawable.cherry_pic))
fruitList.add(Fruit("Mango", R.drawable.mango_pic))
...
}
}Adapter 性能优化过程
这是最初的 Adapter 编写思路:
// 继承与构造函数 - kotlin 基础
class FruitAdapter(activity: Activity, val resourceId: Int, data: List<Fruit>): ArrayAdapter<Fruit>(activity, resourceId, data) {
// 需要加载数据项时调用, 但是每次调用时都会将数据项布局(resourceId)重新加载一遍
override fun getView(position: Int, convertView: View?, parent: ViewGroup): View {
// 加载新的数据项: 使用 LayoutInflater 加载数据项对应的布局
// 第一个参数是要加载的布局文件的 id - 实例化 Adapter 时传入的参数
// 第二个参数是给加载好的布局再添加一个父布局,这里回调函数中带有父布局的 id 直接使用
// 第三个参数为 false 时 ListView 中的标准写法, 表示只让我们在父布局中声明的 layout 属性生效,但不会为这个 View 添加父布局, 因为一旦 View 有了父布局之后,它就不能再添加到 ListView 中了
val view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(resourceId, parent, false)
// 完成 View 的加载即可获取 View 中的组件
val image_fruit_item: ImageView = view.findViewById(R.id.image_fruit_item)
val text_fruit_name:TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_fruit_name)
// 根据 position 加载对应的数据项 - 步骤 1 封装后的实例
val fruit = getItem(position)
// 成功加载后渲染到 view 中
if (fruit != null) {
image_fruit_item.setImageResource(fruit.imageId)
text_fruit_name.text = fruit.name
}
return view
}
}Tips: getView 默认每次调用时都会将数据项布局重新加载一遍, 因此当快速滑动时将会对性能有所影响, 但是每个数据项的布局基本是一致的, 因此我们可以借助对之前布局的缓存 convertView 进行优化
val view: View
if (convertView == null) {
view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(resourceId, parent, false)
} else {
view = convertView
}
// 后续依旧是对布局的数据绑定 ...Tips: 继续观察代码我们发现针对布局中的控件我们每次还是需要 find, 可以借助 ViewHolder 对这部分性能进行优化
// 自定义一个内部类实现对目标控件组的封装
inner class ViewHolder(val fruitImage: ImageView, val fruitName: TextView)
override fun getView(position: Int, convertView: View?, parent: ViewGroup): View {
val view: View
val viewHolder: ViewHolder
// 如果之前不存在 View 的缓存则加载 View 并寻找绑定控件
if (convertView == null) {
view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(resourceId, parent, false)
val image_fruit_item: ImageView = view.findViewById(R.id.image_fruit_item)
val text_fruit_name:TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_fruit_name)
viewHolder = ViewHolder((image_fruit_item, text_fruit_name))
view.tag = viewHolder
} else {
// 否则直接加载
view = convertView
viewHolder = view.tag as ViewHolder
}
val fruit = getItem(position)
if (fruit != null) {
viewHolder.fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.imageId)
viewHolder.fruitName.text = fruit.name
}
return view
}点击事件
ListView 的点击事件会冒泡到 ListView 对象上进行统一处理:
list_main.setOnItemClickListener { adapterView, view, i, l ->
val fruitItem = fruitList[i]
Toast.makeText(this, fruitItem.name, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Tips 不用到的参数可以都使用 _ 替代
list_main.setOnItemClickListener { _, _, i, _ ->
val fruitItem = fruitList[i]
Toast.makeText(this, fruitItem.name, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}RecyclerView
(Why) ListView 在性能, 扩展性等方面存在限制, 因此 Android 提供了更强大的 RecycleView 替代并增强了 ListView(不删除是为了向下适应老版本)
Quick Start
-
准备好数据项的布局
-
创建 Adapter 类:实现 ViewHoder 的声明与定义, 子项的赋值等基本功能
class RecyclerFruitAdapter(val fruitList: List<Fruit>) : RecyclerView.Adapter<RecyclerFruitAdapter.ViewHolder>() {
// 内部类 ViewHolder
// 主构造函数中要传入一个 View 参数 作为 RecyclerView 子项的最外层布局
inner class ViewHolder(view: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(view) {
val fruitImage: ImageView = view.findViewById(R.id.image_fruit_item)
val fruitName: TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_fruit_name)
}
// 创建 ViewHoldedr 实例
// 实现对 子项布局的加载
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.fruit_item, parent, false)
return ViewHolder(view)
}
// 对子项进行赋值
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
val fruit = fruitList[position]
holder.fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.imageId)
holder.fruitName.text = fruit.name
}
// 子项的数目
override fun getItemCount() = fruitList.size
}- 为 RecyclerView 指定父布局和 adapter
val recyclerView = findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.recyclerView)
val layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
recyclerView.layoutManager = layoutManager
val adapter = RecyclerFruitAdapter(fruitList)
recyclerView.adapter = adapter扩展布局
水平排列
- 首先设置好数据子项的布局,至少水平排列时不能占一满行
- 然后再去设置 RecyclerView 的父布局即可
val layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
layoutManager.orientation = LinearLayoutManager.HORIZONTAL
recyclerView.layoutManager = layoutManager瀑布流布局
- 设置好子项的布局
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:id="@+id/image_fruit_item"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/text_fruit_name"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>- 使用
StaggeredGridLayoutManager
val recyclerView = findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.recyclerView)
val layoutManager = StaggeredGridLayoutManager(3, StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL)
recyclerView.layoutManager = layoutManager点击事件
Recycler 为了更精细的控制, 将点击事件的绑定精细到了每一个子项, 在生成子项布局 onCreateViewHolder 时进行定义
// itemView 表示最外层的布局
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.todoitem_card, parent, false)
val holder = ViewHolder(view)
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener {
val position = holder.adapterPosition
val todoItem = todoItemList[position]
startTodoItemInfo(todoItem.id, todoItem.name)
}
return holder
}滑动事件
这里以滑动删除事件为例进行简单介绍
- 首先要建立自己的类, 继承
ItemTouchHelper.XXCallback这些回调方法, 并实现回调处理, 其中 onSwiped 就是滑动的检测; 两个参数分别为拖动的方向(一般实现两个组件间位置交互)与滑动(一般实现目标组件的交互)的方向, 0 表示不可拖动或滑动, 具体方向由 ItemTouchHelper 中的静态属性分配
class BookItemTouchHelperCallback(var adapter: RecyclerBookAdapter): ItemTouchHelper.SimpleCallback(0, ItemTouchHelper.LEFT) {
override fun onMove(
recyclerView: RecyclerView,
viewHolder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder,
target: RecyclerView.ViewHolder
): Boolean {
TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
override fun onSwiped(viewHolder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder, direction: Int) {
var pos = viewHolder.adapterPosition
adapter.deleteItem(pos)
}
}- 然后借助回调方法的实例创建
ItemTouchHelper实例, 并绑定到目标RecyclerView上
val itemTouchHelper = ItemTouchHelper(BookItemTouchHelperCallback(adapter))
itemTouchHelper.attachToRecyclerView(recycler)Android 图标
应用程序的图标应该被分为两层:前景层和背景层
- 前景层用来展示应用图标的 Logo:
- Mask 层: 在图标的前景层和背景层之间, 手机厂商负责定义
- 背景层用来衬托应用图标的 Logo: 只允许定义颜色和纹理,不能定义形状

- res 目录处右击 new/Image_Asssert
- 修改前景的 Logo 图片与背景色

Android 签名文件
Android Studio 生成
- Build/Generate Singed Bundle/APK
- Android App Bundle 文件是用于上架 Google Play 商店的
- APK for Android
- 填入 keystore 文件的路径和密码
- Create New…
- Validity 是 keystore 文件的有效时长,单位是年

Gradle 生成 [Ignore]
- 编辑 app/build.gradle 文件